Potentially synergistic effects of melatonin and metformin in alleviating hyperglycaemia: a comprehensive review
Combination of melatonin and metformin as anti-diabetic therapy
Abstract
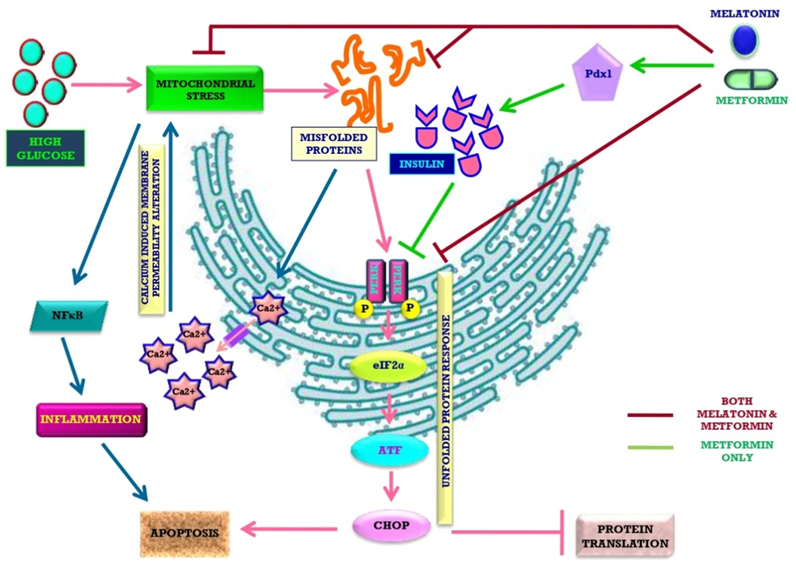
High level of glucose is hazardous for organisms since it leads to lipid peroxidation, protein glycation and free radical generation. Insulin can lower the high blood glucose by promoting cell’s glucose up-taking. Thus, the impeded insulin secretion in type 1-diabetes and insensitivity of cells to insulin in type 2-diabetes cause hyperglycaemia. Hyperglycaemia impairs mitochondrial function of pancreas to trigger ROS generation. The malfunctional mitochondria cause endoplasmic reticulum to produce misfolded non-functional insulin, finally leading to diabetes. Melatonin, the mitochondria targeted antioxidant, provides protection against diabetes by multiple ways. These include balancing cellular redox status, lowering blood glucose level by modulating metabolic pathways and, finally protecting cells/organelles from high glucose induced injury. Moreover, this indoleamine preserves pancreatic physiological normalcy to facilitate insulin secretion. Thus, melatonin can effectively mitigate diabetes and diabetic complications. Metformin, the most prescribed medicine for type 2-diabetes, has similar antidiabetic activities as melatonin. Both the molecules share similar pathways to preserve stress-stricken pancreas and other organs, whereas, melatonin also potentiates the actions of metformin. The potentially synergistic actions of melatonin and metformin are expected and we strongly recommend a combined therapeutic application of these two molecules for treatment of diabetes.
References
2. Robertson RP, Harmon JS (2006) Diabetes, glucose toxicity, and oxidative stress: a case of double jeopardy for the pancreatic islet β cell. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 41 (2): 177-184. DOI: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2005.04.030.
3. Ozougwu JC, Obimba KC, Belonwu CD, Unakalamba CB (2013) The pathogenesis and pathophysiology of type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus. J. Physiol. Pathophysiol. 4 (4): 46-57. DOI: 10.5897/JPAP2013.0001.
4. Asmat U, Abad K, Ismail K (2016) Diabetes mellitus and oxidative stress—A concise review. Saudi Pharm. J. 24 (5): 547-553. DOI: 10.1016/j.jsps.2015.03.013.
5. Pham-HuyLA, He H, Pham-Huy C (2008) Free radicals, antioxidants in disease and health. Int. J. Biomed. Sci. 4 (2): 89-96.PMID: 23675073.
6. Moussa SA. Oxidative stress in diabetes mellitus (2008) Romanian J. Biophys. 18 (3): 225-236.
7. Back SH, Kaufman RJ (2012) Endoplasmic reticulum stress and type 2 diabetes. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 81: 767-793. DOI: 10.1146/annurev-biochem-072909-095555.
8. Feher MD, Al-Mrayat ME, Brake J, Leong KS (2007) Tolerability of prolonged-release metformin (Glucophage® SR) in individuals intolerant to standard metformin—results from four UK centres. Br. J. Diabetes Vasc. Dis. 7 (5): 225-228. DOI: 10.1177/14746514070070050501.
9. Cryer DR, Nicholas SP, Henry DH, Mills DJ, Stadel BV (2005) Comparative outcomes study of metformin intervention versus conventional approach the COSMIC Approach Study. Diabetes Care 28 (3): 539-543. DOI:10.2337/diacare.28.3.539.
10. Esteghamati A, Eskandari D, Mirmiranpour H, Noshad S, Mousavizadeh M, Hedayati M, Nakhjavani M (2013) Effects of metformin on markers of oxidative stress and antioxidant reserve in patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes: a randomized clinical trial. Clin. Nutr. 32 (2): 179-185. DOI: 10.1016/j.clnu.2012.08.006.
11. Wright AD, Cull CA, Macleod KM, Holman RR, UKPDS Group (2006) Hypoglycemia in type 2 diabetic patients randomized to and maintained on monotherapy with diet, sulfonylurea, metformin, or insulin for 6 years from diagnosis: UKPDS73. J. Diabetes Complicat. 20 (6): 395-401. DOI: 10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2005.08.010.
12. Hostalek U, Gwilt M, Hildemann S (2015) Therapeutic use of metformin in prediabetes and diabetes prevention. Drugs 75 (10): 1071-1094. DOI: 10.1007/s40265-015-0416-8.
13. Galano A, Tan DX, Reiter RJ (2011) Melatonin as a natural ally against oxidative stress: a physicochemical examination. J. Pineal Res. 51 (1): 1-6. DOI: 10.1111/j.1600-079X.2011.00916.x.
14. Cagnacci A, Arangino S, Renzi A, Paoletti AM, Melis GB, Cagnacci P, Volpe A (2001) Influence of melatonin administration on glucose tolerance and insulin sensitivity of postmenopausal women. Clin. Endocrinol. 54 (3): 339-346. DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2265.2001.01232.x.
15. Banerjee A, Chattopadhyay A, Bandyopadhyay D (2020) Biorhythmic and receptor mediated interplay between melatonin and insulin: its consequences on diabetic erythrocytes. Melatonin Res. 3 (2): 243-263. DOI: 10.32794/mr12250060.
16. Nishida S (2005) Metabolic effects of melatonin on odative stress and diabetes mellitus. Endocrine 27 (2): 131-135. DOI: 10.1385/endo:27:2:131.
17. Aouichat S, Navarro-Alarcon M, Alarcón-Guijo P, Salagre D, Ncir M, Zourgui L, Agil A (2021) Melatonin Improves Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress-Mediated IRE1α Pathway in Zücker Diabetic Fatty Rat. Pharmaceuticals 14 (3): 232. DOI: 10.3390/ph14030232.
18. Abdulwahab DA, El-Missiry MA, Shabana S, Othman AI, Amer ME (2021) Melatonin protects the heart and pancreas by improving glucose homeostasis, oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis in T2DM-induced rats. Heliyon 7 (3): e06474. DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e06474.
19. Dantas‐Ferreira RF, Raingard H, Dumont S, Schuster‐Klein C, Guardiola‐Lemaitre B, Pevet P, Challet E (2018) Melatonin potentiates the effects of metformin on glucose metabolism and food intake in high‐fat‐fed rats. Endocrinol. Diabetes Metab. 1 (4): e00039. DOI: 10.1002/edm2.39.
20. Thomas AP, Hoang J, Vongbunyong K, Nguyen A, Rakshit K, Matveyenko AV (2016) Administration of melatonin and metformin prevents deleterious effects of circadian disruption and obesity in male rats. Endocrinology 157 (12): 4720-4731. DOI: 10.1210/en.2016-1309.
21. Ceriello A (2000) Oxidative stress and glycemic regulation. Metabolism 49 (2): 27-29. DOI: 10.1016/s0026-0495(00)80082-7.
22. Baynes JW, Thorpe SR (1999) Role of oxidative stress in diabetic complications: a new perspective on an old paradigm. Diabetes 48 (1): 1-9. DOI: 10.2337/diabetes.48.1.1.
23. Baynes JW (1991) Role of oxidative stress in development of complications in diabetes. Diabetes 40 (4): 405-412. DOI: 10.2337/diab.40.4.405.
24. Jiang ZY, Woollard AC, Wolff SP (1990) Hydrogen peroxide production during experimental protein glycation. FEBS Lett. 268 (1): 69-71. DOI: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80974-n.
25. Wolff SP, Dean RT (1987) Glucose autoxidation and protein modification. The potential role of ‘autoxidative glycosylation’in diabetes. Biochem. J. 245 (1): 243-250. DOI: 10.1042/bj2450243.
26. Hogg N, Kalyanaraman B, Joseph J, Struck A, Parthasarathy S (1993) Inhibition of low‐density lipoprotein oxidation by nitric oxide Potential role in atherogenesis. FEBS Lett. 334 (2): 170-174. DOI: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)81706-6.
27. Tsai EC, Hirsch IB, Brunzell JD, Chait A (1994) Reduced plasma peroxyl radical trapping capacity and increased susceptibility of LDL to oxidation in poorly controlled IDDM. Diabetes 43 (8): 1010-1014. DOI: 10.2337/diab.43.8.1010.
28. Kawamura M, Heinecke JW, Chait A (1994) Pathophysiological concentrations of glucose promote oxidative modification of low density lipoprotein by a superoxide-dependent pathway. J.Clin. Invest. 94 (2): 771-778. DOI: 10.1172/JCI117396.
29. Nishikawa T, Edelstein D, Du XL, Yamagishi SI, Matsumura T, Kaneda Y, Yorek MA, Beebe D, Oates PJ, Hammes HP, Giardino I (2000) Normalizing mitochondrial superoxide production blocks three pathways of hyperglycaemic damage. Nature 404 (6779): 787-790. DOI: 10.1038/35008121.
30. Petrova R, Yamamoto Y, Muraki K, Yonekura H, Sakurai S, Watanabe T, Li H, Takeuchi M, Makita Z, Kato I, Takasawa S (2002) Advanced glycation endproduct-induced calcium handling impairment in mouse cardiac myocytes. J. Mol. Cell Cardiol. 34 (10): 1425-1431. DOI: 10.1006/jmcc.2002.2084.
31. Sugimoto K, Nishizawa Y, Horiuchi S, Yagihashi S (1997) Localization in human diabetic peripheral nerve of N (epsilon) -Carboxymethyllysine protein adducts, an advanced glycation end product. Diabetologia 40 (12): 1380-1387. DOI:10.1007/s001250050839.
32. Goldin A, Beckman JA, Schmidt AM, Creager MA (2006) Advanced glycation end products: sparking the development of diabetic vascular injury. Circulation. 114 (6): 597-605. DOI: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.106.621854.
33. Giacco F, Brownlee M (2010) Oxidative stress and diabetic complications. Circ. Res. 107 (9): 1058-1070. DOI: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.110.223545.
34. Du XL, Edelstein D, Rossetti L, Fantus IG, Goldberg H, Ziyadeh F, Wu J, Brownlee M (2000)Hyperglycemia-induced mitochondrial superoxide overproduction activates the hexosamine pathway and induces plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 expression by increasing Sp1 glycosylation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 97 (22): 12222-12226. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.97.22.12222.
35. Wallace DC (1992) Diseases of the mitochondrial DNA. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 61 (1): 1175-1212. DOI: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.005523.
36. Kowluru RA, Kowluru V, Xiong Y, Ho YS (2006) Overexpression of mitochondrial superoxide dismutase in mice protects the retina from diabetes-induced oxidative stress. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 41 (8): 1191-1196. DOI: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2006.01.012.
37. Ceradini DJ, Yao D, Grogan RH, Callaghan MJ, Edelstein D, Brownlee M, Gurtner GC (2008) Decreasing intracellular superoxide corrects defective ischemia-induced new vessel formation in diabetic mice. J. Biol. Chem. 283 (16): 10930-10938. DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M707451200.
38. Rolo AP, Palmeira CM (2006) Diabetes and mitochondrial function: role of hyperglycemia and oxidative stress. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 212 (2): 167-178. DOI: 10.1016/j.taap.2006.01.003.
39. Brownlee M (2001) Biochemistry and molecular cell biology of diabetic complications. Nature 414 (6865): 813-820. DOI: 10.1038/414813a.
40. Ansari NA, Dash D (2013) Amadori glycated proteins: role in production of autoantibodies in diabetes mellitus and effect of inhibitors on non-enzymatic glycation. Aging Dis. 4 (1): 50-56. PMID: 23423609.
41. Welsh KJ, Kirkman MS, Sacks DB (2016) Role of glycated proteins in the diagnosis and management of diabetes: research gaps and future directions. Diabetes Care 39 (8): 1299-1306. DOI: 10.2337/dc15-2727.
42. Santos DL, Palmeira CM, Sei R, Dias J, Mesquita J, Moreno AJ, Santos MS (2003) Diabetes and mitochondrial oxidative stress: a study using heart mitochondria from the diabetic Goto-Kakizaki rat. Mol. Cell Biochem. 246 (1): 163-170. DOI: 10.1023/A:1023475022025.
43. Green K, Brand MD, Murphy MP (2004) Prevention of mitochondrial oxidative damage as a therapeutic strategy in diabetes. Diabetes 53 (suppl 1): S110-8. DOI: 10.2337/diabetes.53.2007.s110.
44. Mooradian AD, Haas MJ (2011) Glucose-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress is independent of oxidative stress: a mechanistic explanation for the failure of antioxidant therapy in diabetes. Free Radic. Biol. Med .50 (9): 1140-1143. DOI: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2011.02.002.
45. Laybutt DR, Preston AM, Åkerfeldt MC, Kench JG, Busch AK, Biankin AV, Biden TJ (2007) Endoplasmic reticulum stress contributes to beta cell apoptosis in type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia 50 (4): 752-763. DOI: 10.1007/s00125-006-0590-z.
46. Harding HP, Ron D (2002) Endoplasmic reticulum stress and the development of diabetes: a review. Diabetes. 51 (suppl 3): S455-S461. DOI: 10.2337/diabetes.51.2007.s455.
47. Oyadomari S, Takeda K, Takiguchi M, Gotoh T, Matsumoto M, Wada I, Akira S, Araki E, Mori M (2001) Nitric oxide-induced apoptosis in pancreatic β cells is mediated by the endoplasmic reticulum stress pathway. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 98 (19): 10845-10850. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.191207498.
48. Oyadomari S, Koizumi A, Takeda K, Gotoh T, Akira S, Araki E, Mori M (2002) Targeted disruption of the Chop gene delays endoplasmic reticulum stress–mediated diabetes. J. Clin. Invest. 109 (4): 525-532. DOI: 10.1172/JCI14550.
49. Flamment M,Hajduch E, Ferré P, Foufelle F (2012) New insights into ER stress-induced insulin resistance. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 23 (8): 381-390. DOI: 10.1016/j.tem.2012.06.003.
50. Hu M, Phan F, Bourron O, Ferré P, Foufelle F (2017) Steatosis and NASH in type 2 diabetes. Biochimie 143: 37-41. DOI: 10.1016/j.biochi.2017.10.019.
51. Özcan U, Yilmaz E, Özcan L, Furuhashi M, Vaillancourt E, Smith RO, Görgün CZ, Hotamisligil GS (2006) Chemical chaperones reduce ER stress and restore glucose homeostasis in a mouse model of type 2 diabetes. Science 313 (5790): 1137-40. DOI: 10.1126/science.1128294.
52. Plaisance V, Brajkovic S, Tenenbaum M, Favre D, Ezanno H, Bonnefond A, Bonner C, Gmyr V, Kerr-Conte J, Gauthier BR, Widmann C (2016) Endoplasmic reticulum stress links oxidative stress to impaired pancreatic beta-cell function caused by human oxidized LDL. PLoS One 11(9): e0163046. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0163046.
53. Dowling P, O'Driscoll L, O'Sullivan F, Dowd A, Henry M, Jeppesen PB, Meleady P, Clynes M (2006) Proteomic screening of glucose‐responsive and glucose non‐responsive MIN‐6 beta cells reveals differential expression of proteins involved in protein folding, secretion and oxidative stress. Proteomics 6 (24): 6578-6587. DOI: 10.1002/pmic.200600298.
54. Cao SS, Kaufman RJ (2014) Endoplasmic reticulum stress and oxidative stress in cell fate decision and human disease. Antioxid. Redox. Signal. 21 (3): 396-413. DOI: 10.1089/ars.2014.5851.
55. Maamoun H, Abdelsalam SS,Zeidan A, Korashy HM, Agouni A (2019) Endoplasmic reticulum stress: a critical molecular driver of endothelial dysfunction and cardiovascular disturbances associated with diabetes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 20 (7): 1658. DOI: 10.3390/ijms20071658.
56. Hasnain SZ, Prins JB, McGuckin MA (2016) Oxidative and endoplasmic reticulum stress in b-cell dysfunction in diabetes. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 56 (2): 33-54. DOI: 10.1530/JME-15-0232.
57. Gardner BM, Pincus D, Gotthardt K, Gallagher CM, Walter P (2013) Endoplasmic reticulum stress sensing in the unfolded protein response. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 5 (3): a013169. DOI: 10.1101/cshperspect.a013169.
58. Gardner BM, Walter P (2011) Unfolded proteins are Ire1-activating ligands that directly induce the unfolded protein response. Science 333 (6051): 1891-1894. DOI: 10.1126/science.1209126.
59. Walter P, Ron D (2011) The unfolded protein response: from stress pathway to homeostatic regulation. Science 334 (6059): 1081-1086. DOI: 10.1126/science.1209038.
60. Marciniak SJ, Yun CY, Oyadomari S, Novoa I, Zhang Y, Jungreis R, Nagata K, Harding HP, Ron D (2004) CHOP induces death by promoting protein synthesis and oxidation in the stressed endoplasmic reticulum. Genes Dev. 18 (24): 3066-3077. DOI: 10.1101/gad.1250704.
61. Chen Y, Wang JJ, Li J, Hosoya KI, Ratan R, Townes T, Zhang SX (2012) Activating transcription factor 4 mediates hyperglycaemia-induced endothelial inflammation and retinal vascular leakage through activation of STAT3 in a mouse model of type 1 diabetes. Diabetologia 55 (9): 2533-2545. DOI: 10.1007/s00125-012-2594-1.
62. Sun J, Cui J, He Q, Chen Z, Arvan P, Liu M (2015) Proinsulin misfolding and endoplasmic reticulum stress during the development and progression of diabetes. Mol. Aspects Med. 42: 105-118. DOI: 10.1016/j.mam.2015.01.001.
63. Hara T, Mahadevan J, Kanekura K, Hara M, Lu S, Urano F (2014) Calcium efflux from the endoplasmic reticulum leads to β-cell death. Endocrinology 155 (3): 758-768. DOI: 10.1210/en.2013-1519.
64. Lowell BB, Shulman GI (2005) Mitochondrial dysfunction and type 2 diabetes. Science 307 (5708): 384-387. DOI: 10.1126/science.1104343.
65. Supale S, Li N, Brun T, Maechler P (2012) Mitochondrial dysfunction in pancreatic β cells. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 23 (9): 477-487. DOI: 10.1016/j.tem.2012.06.002. DOI: 10.1016/j.tem.2012.06.002.
66. Rolo AP, Palmeira CM (2006) Diabetes and mitochondrial function: role of hyperglycemiaand oxidative stress. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 212 (2): 167-178. DOI: 10.1016/j.taap.2006.01.003.
67. Acharya JD, Ghaskadbi SS (2010) Islets and their antioxidant defense. Islets 2 (4): 225-235. DOI: 10.4161/isl.2.4.12219.
68. Lenzen S (2008) Oxidative stress: the vulnerable β-cell. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 36 (3): 343-347. DOI: 10.1042/BST0360343.
69. Robertson RP (2004) Chronic oxidative stress as a central mechanism for glucose toxicity in pancreatic islet beta cells in diabetes. J. Biol. Chem. 279 (41): 42351-42354. DOI: 10.1074/jbc.R400019200.
70. Kajimoto Y, Kaneto H (2004) Role of oxidative stress in pancreatic β-cell dysfunction. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1011: 168-176. DOI: 10.1007/978-3-662-41088-2_17.
71. Kakkar R, Mantha SV, Radhi J, Prasad K, Kalra J (1998) Increased oxidative stress in rat liver and pancreas during progression of streptozotocin-induced diabetes. Clin. Sci. 94 (6): 623-632. DOI: 10.1042/cs0940623.
72. Kaneto H, Kawamori D, Matsuoka TA, Kajimoto Y, Yamasaki Y (2005) Oxidative stress and pancreatic β-cell dysfunction. Am. J. Ther. 12 (6): 529-533. DOI: 10.1097/01.mjt.0000178773.31525.c2.
73. Wang J, Wang H (2017) Oxidative stress in pancreatic beta cell regeneration. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2017: 1930261. DOI: 10.1155/2017/1930261.
74. Ihara Y, Toyokuni S, Uchida K, Odaka H, Tanaka T, Ikeda H, Hiai H (1999) Hyperglycaemia causes oxidative stress in pancreatic (B-Cells of GK Rats, a Model of type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 48 (4): 927-932. DOI: 10.2337/diabetes.48.4.927.
75. Baydas G, Canatan H, Turkoglu A (2002) Comparative analysis of the protective effects of melatonin and vitamin E on streptozocin‐induced diabetes mellitus. J. Pineal Res. 32 (4): 225-230. DOI: 10.1034/j.1600-079x.2002.01856.x.
76. Montilla PL, Vargas JF, Túnez IF, Carmen M, de Agueda M, Valdelvira ME, Cabrera ES (1998) Oxidative stress in diabetic rats induced by streptozotocin: protective effects of melatonin. J. Pineal Res.25 (2): 94-100. DOI: 10.1111/j.1600-079x.1998.tb00545.x.
77. Espino J, Pariente JA, Rodríguez AB (2011) Role of melatonin on diabetes-related metabolic disorders. World J. Diabetes 2 (6): 82-91. DOI: 10.4239/wjd.v2.i6.82.
78. Brömme HJ, Ebelt H, Peschke D, Peschke E (1999) Alloxan acts as a prooxidant only under reducing conditions: influence of melatonin. Cellular Mol. Life Sci. 55 (3): 487-493. DOI: 10.1007/s000180050305.
79. Štetinová V, Smetanová L, Grossmann V, Anzenbacher P (2002) In vitro and in vivo assessment of the antioxidant activity of melatonin and related indole derivatives. Gen. Physiol. Biophys. 21 (2): 153-162. DOI: DOI 10.1007/s10238-004-0050-3.
80. Winiarska K, Fraczyk T, Malinska D, Drozak J, Bryla J (2006) Melatonin attenuates diabetes‐induced oxidative stress in rabbits. J. Pineal Res. 40 (2): 168-176. DOI: 10.1111/j.1600-079X.2005.00295.x.
81. Brömme HJ, Mörke W, Peschke E, Ebelt H, Peschke D (2000) Scavenging effect of melatonin on hydroxyl radicals generated by alloxan. J. Pineal Res. 29 (4): 201-208. DOI: 10.1034/j.1600-0633.2002.290402.x.
82. Ebelt H, Peschke D, BrömmeHJ, Mörke W, Blume R, Peschke E (2000) Influence of melatonin on free radical‐induced changes in rat pancreatic beta‐cells in vitro. J. Pineal Res. 28 (2): 65-72. DOI: 10.1034/j.1600-079x.2001.280201.x.
83. Park JH, Shim HM, Na AY, Bae KC, Bae JH, Im SS, Cho HC, Song DK (2014) Melatonin prevents pancreatic β‐cell loss due to glucotoxicity: the relationship between oxidative stress and endoplasmic reticulum stress. J. Pineal Res. 56 (2): 143-153. DOI: 10.1111/jpi.12106.
84. Yavuz O, Cam M, Bukan N, Guven A, Silan F (2003) Protective effect of melatonin on β-cell damage in streptozotocin-induced diabetes in rats. Acta histochem. 105 (3): 261-266.
85. Kanter M, Uysal H, Karaca T, Sagmanligil HO (2006) Depression of glucose levels and partial restoration of pancreatic β-cell damage by melatonin in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Arch. Toxicol. 80 (6): 362-369. DOI: 10.1007/s00204-005-0055-z.
86. Zephy D, Ahmad J (2015) Type 2 diabetes mellitus: role of melatonin and oxidative stress. Diabetes Metab.Syndr. 9 (2): 127-131. DOI: 10.1016/j.dsx.2014.09.018.
87. Espino J, Rodríguez AB, Pariente JA (2019) Melatonin and oxidative stress in the diabetic state: clinical implications and potential therapeutic applications. Curr. Med. Chem. 26 (22): 4178-4190. DOI: 10.2174/0929867325666180410094149.
88. Doosti-Irani A, Ostadmohammadi V, Mirhosseini N, Mansournia MA, Reiter RJ, Kashanian M, Rahimi M, Razavi M, Asemi Z (2018) The effects of melatonin supplementation on glycemic control: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Horm. Metab. Res. 50 (11): 783-790. DOI: 10.1055/a-0752-8462.
89. Guven A, Yavuz O, Cam M, Ercan F, Bukan N, Comunoglu C, Gokce F (2006) Effects of melatonin on streptozotocin-induced diabetic liver injury in rats. Acta Histochem. 108 (2): 85-93. DOI: 10.1016/j.acthis.2006.03.005.
90. Lenk SE, Bhat D, Blakeney W, Dunn Jr WA (1992) Effects of streptozotocin-induced diabetes on rough endoplasmic reticulum and lysosomes of rat liver. Am. J. Physiol. 263 (5): E856-E862. DOI: 10.1152/ajpendo.1992.263.5.E856.
91. Zhou R, Ma Y, Tao Z, Qiu S, Gong Z, Tao L, Zhu Y (2020) Melatonin Inhibits Glucose-Induced Apoptosis in Osteoblastic Cell Line Through PERK-eIF2α-ATF4 Pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 11: 602307. DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2020.602307.
92. Lima FB, Machado UF, Bartol I, Seraphim PM, Sumida DH, Moraes SM, Hell NS, Okamoto MM, Saad MJ, Carvalho CR, Cipolla-Neto J (1998) Pinealectomy causes glucose intolerance and decreases adipose cell responsiveness to insulin in rats. Am. J. Physiol. 275 (6): E934-941. DOI: 10.1152/ajpendo.1998.275.6.E934.
93. Alonso-Vale MI, Borges-Silva CN, Anhe GF, Andreotti S, Machado MA, Cipolla-Neto J, Lima FB (2004) Light/dark cycle-dependent metabolic changes in adipose tissue of pinealectomized rats. Horm. Metab. Res. 36 (07): 474-479. DOI: 10.1055/s-2004-825723.
94. Nogueira TC, Lellis-Santos C, Jesus DS, Taneda M, Rodrigues SC, Amaral FG, Lopes AM, Cipolla-Neto J, Bordin S, Anhê GF (2011) Absence of melatonin induces night-time hepatic insulin resistance and increased gluconeogenesis due to stimulation of nocturnal unfolded protein response. Endocrinology 152 (4): 1253-1263. DOI: 10.1210/en.2010-1088.
95. Faria JA, Kinote A, Ignacio-Souza LM, de Araújo TM, Razolli DS, Doneda DL, Paschoal LB, Lellis-Santos C, Bertolini GL, Velloso LA, Bordin S (2013) Melatonin acts through MT1/MT2 receptors to activate hypothalamic Akt and suppress hepatic gluconeogenesis in rats. Am. J. Physiol. 305 (2): E230-E242. DOI: 10.1152/ajpendo.00094.2013.
96. Sudnikovich EJ, Maksimchik YZ, Zabrodskaya SV, Kubyshin VL, Lapshina EA, Bryszewska M, Reiter RJ, Zavodnik IB (2007) Melatonin attenuates metabolic disorders due to streptozotocin-induced diabetes in rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 569 (3): 180-187. DOI: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2007.05.018
97. Pierrefiche G, Laborit H (1995) Oxygen free radicals, melatonin, and aging. Exp. Gerontol. 30 (3-4): 213-227. DOI: 10.1016/0531-5565(94)00036-3.
98. Winiarska K, Dzik JM, Labudda M, Focht D, Sierakowski B, Owczarek A, Komorowski L, Bielecki W (2016) Melatonin nephroprotective action in Zucker diabetic fatty rats involves its inhibitory effect on NADPH oxidase. J. Pineal Res. 60 (1): 109-117. DOI: 10.1111/jpi.12296.
99. Simões D, Riva P, Peliciari-Garcia RA, Cruzat VF, Graciano MF, Munhoz AC, Taneda M, Cipolla-Neto J, Carpinelli AR (2016) Melatonin modifies basal and stimulated insulin secretion via NADPH oxidase. J Endocrinol. 231 (3): 235-244. DOI: 10.1530/JOE-16-0259.
100. Winiarska K, Jarzyna R, Dzik JM, Jagielski AK, Grabowski M, Nowosielska A, Focht D, Sierakowski B (2015) ERK1/2 pathway is involved in renal gluconeogenesis inhibition under conditions of lowered NADPH oxidase activity. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 81: 13-21. DOI: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2014.12.024.
101. Agil A, El‐Hammadi M, Jiménez‐Aranda A, Tassi M, Abdo W, Fernández‐Vázquez G, Reiter RJ (2015) Melatonin reduces hepatic mitochondrial dysfunction in diabetic obese rats. J. Pineal Res. 59 (1): 70-79. DOI: 10.1111/jpi.12241.
102. Agil A, Rosado I, Ruiz R, Figueroa A, Zen N, Fernández‐Vázquez G (2012) Melatonin improves glucose homeostasis in young Zucker diabetic fatty rats. J. Pineal Res. 52 (2): 203-210. DOI: 10.1111/j.1600-079X.2011.00928.x.
103. Martyn JA, Kaneki M, Yasuhara S, Warner DS, Warner MA (2008) Obesity-induced insulin resistance and hyperglycemia: etiologic factors and molecular mechanisms. Anesthesiology 109 (1): 137-148. DOI: 10.1097/ALN.0b013e3181799d45.
104. Wellen KE, Hotamisligil GS (2005) Inflammation, stress, and diabetes. J. Clin. Invest. 115 (5): 1111-1119. DOI: 10.1172/JCI25102.
105. Saltiel AR, Kahn CR (2001) Insulin signalling and the regulation of glucose and lipid metabolism. Nature 414 (6865): 799-806.
106. Cinti S, Mitchell G, Barbatelli G, Murano I, Ceresi E, Faloia E, Wang S, Fortier M, Greenberg AS, Obin MS (2005) Adipocyte death defines macrophage localization and function in adipose tissue of obese mice and humans. J. Lipid Res. 46 (11): 2347-2355. DOI: 10.1194/jlr.M500294-JLR200.
107. Özcan U, Cao Q, Yilmaz E, Lee AH, Iwakoshi NN, Özdelen E, Tuncman G, Görgün C, Glimcher LH, Hotamisligil GS (2004) Endoplasmic reticulum stress links obesity, insulin action, and type 2 diabetes. Science 306 (5695): 457-461. DOI: 10.1126/science.1103160.
108. Navarro-Alarcón M, Gil-Hernández F, Sánchez-González C, Llopis J, Villalón-Mir M, Olmedo P, Alarcón-Guijo P, Salagre D, Gaona L, Paredes M, Agil A (2021) Melatonin improves levels of Zn and Cu in the muscle of diabetic obese rats. Pharmaceutics 13 (10): 1535. DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13101535.
109. Fernández Vázquez G, Reiter RJ, Agil A (2018) Melatonin increases brown adipose tissue mass and function in Zücker diabetic fatty rats: implications for obesity control. J. Pineal Res. 64 (4): e12472. DOI: 10.1111/jpi.12472.
110. Promsan S, Lungkaphin A (2020) The roles of melatonin on kidney injury in obese and diabetic conditions. BioFactors 46 (4): 531-549. DOI: 10.1002/biof.1637.
111. Agil A, Chayah M, Visiedo L, Navarro-Alarcon M, Rodríguez Ferrer JM, Tassi M, Reiter RJ, Fernández-Vázquez G (2020) Melatonin improves mitochondrial dynamics and function in the kidney of zücker diabetic fatty rats. J. Clin. Med .9 (9): 2916. DOI: 10.3390/jcm9092916.
112. Tsalamandris S, Antonopoulos AS, Oikonomou E, Papamikroulis GA, Vogiatzi G, Papaioannou S, Deftereos S, Tousoulis D (2019) The role of inflammation in diabetes: current concepts and future perspectives. Eur. Cardiol. 14 (1): 50. DOI: 10.15420/ecr.2018.33.1.
113. Feuerer M, Shen Y, Littman DR, Benoist C, Mathis D (2009) How punctual ablation of regulatory T cells unleashes an autoimmune lesion within the pancreatic islets. Immunity 31 (4): 654-664. DOI: 10.1016/j.immuni.2009.08.023.
114. Moore F, Colli ML, Cnop M, Esteve MI, Cardozo AK, Cunha DA, Bugliani M, Marchetti P, Eizirik DL (2009) PTPN2, a candidate gene for type 1 diabetes, modulates interferon-γ–induced pancreatic β-cell apoptosis. Diabetes 58 (6): 1283-1291. DOI: 10.2337/db08-1510.
115. Leibowitz G, Bachar E, Shaked M, Sinai A, Ketzinel‐Gilad M, Cerasi E, Kaiser N (2010) Glucose regulation of β‐cell stress in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes. Metab .12: 66-75. DOI: 10.1111/j.1463-1326.2010.01280.x.
116. Willcox A, Richardson SJ, Bone AJ, Foulis AK, Morgan NG (2009) Analysis of islet inflammation in human type 1 diabetes. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 155 (2): 173-181. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2008.03860.x.
117. Lehuen A, Diana J, Zaccone P, Cooke A (2010) Immune cell crosstalk in type 1 diabetes. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 10 (7): 501-513. DOI: 10.1038/nri2787.
118. Hotamisligil GS (2006) Inflammation and metabolic disorders. Nature 444 (7121): 860-867. DOI: 10.1038/nature05485.
119. Olefsky JM, Glass CK (2010) Macrophages, inflammation, and insulin resistance. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 72: 219-246. DOI: 10.1146/annurev-physiol-021909-135846.
120. Lumeng CN, Saltiel AR (2011) Inflammatory links between obesity and metabolic disease. J. Clin. Invest. 121 (6): 2111-2117. DOI: 10.1172/JCI57132.
121. Hirosumi J, Tuncman G, Chang L, Görgün CZ, Uysal KT, Maeda K, Karin M, Hotamisligil GS (2002) A central role for JNK in obesity and insulin resistance. Nature 420 (6913): 333-336. DOI: 10.1038/nature01137.
122. Hotamisligil GS, Shargill NS, Spiegelman BM (1993) Adipose expression of tumor necrosis factor-alpha: direct role in obesity-linked insulin resistance. Science 259 (5091): 87-91.DOI: 10.1126/science.7678183.
123. Pradhan AD, Manson JE, Rifai N, Buring JE, Ridker PM (2001) C-reactive protein, interleukin 6, and risk of developing type 2 diabetes mellitus. Jama 286 (3): 327-334. DOI: 10.1001/jama.286.3.327.
124. Donath MY, Shoelson SE (2011) Type 2 diabetes as an inflammatory disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 11 (2): 98-107. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nri2925.
125. Rehman K, Akash MS, Liaqat A, Kamal S, Qadir MI, Rasul A (2017) Role of interleukin-6 in development of insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Crit. Rev. Eukaryot. Gene Expr. 27 (3): 229-236. DOI: 10.1615/CritRevEukaryotGeneExpr.2017019712.
126. Larsen CM, Faulenbach M, Vaag A, Vølund A, Ehses JA, Seifert B, Mandrup-Poulsen T, Donath MY (2007) Interleukin-1–receptor antagonist in type 2 diabetes mellitus. N. Engl. J. Med. 356 (15): 1517-1526. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa065213.
127. Ehses JA, Lacraz G, Giroix MH, Schmidlin F, Coulaud J, Kassis N, Irminger JC, Kergoat M, Portha B, Homo-Delarche F, Donath MY (2009) IL-1 antagonism reduces hyperglycemia and tissue inflammation in the type 2 diabetic GK rat. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 106 (33): 13998-14003. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0810087106.
128. Shoelson SE, Herrero L, Naaz A (2007) Obesity, inflammation, and insulin resistance. Gastroenterol. 132 (6): 2169-2180. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2007.03.059.
129. Kanda H, Tateya S, Tamori Y, Kotani K, Hiasa KI, Kitazawa R, Kitazawa S, Miyachi H, Maeda S, Egashira K, Kasuga M (2006) MCP-1 contributes to macrophage infiltration into adipose tissue, insulin resistance, and hepatic steatosis in obesity. J. Clin. Invest. 116 (6): 1494-1505. DOI: 10.1172/JCI26498.
130. Antonopoulos AS, Margaritis M, Coutinho P, Shirodaria C, Psarros C, Herdman L, Sanna F, De Silva R, Petrou M, Sayeed R, Krasopoulos G (2015) Adiponectin as a link between type 2 diabetes and vascular NADPH oxidase activity in the human arterial wall: the regulatory role of perivascular adipose tissue. Diabetes 64 (6): 2207-2219. DOI: 10.2337/db14-1011.
131. Nikolajczyk BS, Jagannathan-Bogdan M, Shin H, Gyurko R (2011) State of the union between metabolism and the immune system in type 2 diabetes. Genes Immun.12 (4): 239-250. DOI: 10.1038/gene.2011.14.
132. Hardeland R (2018) Melatonin and inflammation—Story of a double‐edged blade. J. Pineal Res. 65 (4): e12525. DOI: 10.1111/jpi.12525.
133. Tarocco A, Caroccia N, Morciano G, Wieckowski MR, Ancora G, Garani G, Pinton P (2019) Melatonin as a master regulator of cell death and inflammation: molecular mechanisms and clinical implications for newborn care. Cell Death Dis. 10 (4): 1-2. DOI: 10.1038/s41419-019-1556-7.
134. Reiter RJ, Calvo JR, Karbownik M, Qi W, Tan DX (2000) Melatonin and its relation to the immune system and inflammation. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 917 (1): 376-386. DOI: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2000.tb05402.x.
135. Favero G, Franceschetti L, Bonomini F, Rodella LF, Rezzani R (2017) Melatonin as an anti-inflammatory agent modulating inflammasome activation. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2017: 1835195. DOI: 10.1155/2017/1835195.
136. Reiter RJ, Mayo JC, Tan DX, Sainz RM, Alatorre‐Jimenez M, Qin L (2016) Melatonin as an antioxidant: under promises but over delivers. J. Pineal Res. 61 (3): 253-278. DOI: 10.1111/jpi.12360.
137. Sharma A, Tate M, Mathew G, Vince JE, Ritchie RH, De Haan JB (2018) Oxidative stress and NLRP3-inflammasome activity as significant drivers of diabetic cardiovascular complications: therapeutic implications. Front. Physiol. 9: 114. DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2018.00114.
138. El-Missiry MA, El-Missiry ZM (2020) Melatonin is a potential adjuvant to improve clinical outcomes in individuals with obesity and diabetes with coexistence of Covid-19. Eur.J. Pharmacol. 882: 173329. DOI: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2020.173329.
139. Xu H, Barnes GT, Yang Q, Tan G, Yang D, Chou CJ, Sole J, Nichols A, Ross JS, Tartaglia LA, Chen H (2003) Chronic inflammation in fat plays a crucial role in the development of obesity-related insulin resistance. J. Clin. Invest. 112 (12): 1821-1830. DOI: 10.1172/JCI19451.
140. Pourhanifeh MH, Hosseinzadeh A, Dehdashtian E, Hemati K, Mehrzadi S (2020) Melatonin: new insights on its therapeutic properties in diabetic complications. Diab. Metab. Syndr. 12: 1-20. DOI: 10.1186/s13098-020-00537-z.
141. Devereux RB, Roman MJ, Paranicas M, O’Grady MJ, Lee ET, Welty TK, Fabsitz RR, Robbins D, Rhoades ER, Howard BV (2000) Impact of diabetes on cardiac structure and function: the strong heart study. Circulation 101 (19): 2271-2276. DOI: 0.1161/01.cir.101.19.2271.
142. Wold LE, Ceylan‐Isik AF, Ren J (2005) Oxidative stress and stress signaling: menace of diabetic cardiomyopathy. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 26 (8): 908-917. DOI: 10.1111/j.1745-7254.2005.00146.x.
143. Kandemir YB, Guntekin Ü, Tosun V, Korucuk N, Bozdemir MN (2018) Melatonin protects against streptozotocin-induced diabetic cardiomyopathy by the phosphorylation of vascular endothelial growth factor-A (VEGF-A). Cell Mol. Biol. 64 (14): 47-52. DOI: 10.14715/cmb/2018.64.14.8.
144. Kandemir YB, Tosun V, Güntekin Ü (2019) Melatonin protects against streptozotocin-induced diabetic cardiomyopathy through the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) signaling pathway. Adv. Clin. Exp. Med. 28 (9): 1171-1177. DOI: 10.17219/acem/103799.
145. Yu LM, Di WC, Dong X, Li Z, Zhang Y, Xue XD, Xu YL, Zhang J, Xiao X, Han JS, Liu Y (2018) Melatonin protects diabetic heart against ischemia-reperfusion injury, role of membrane receptor-dependent cGMP-PKG activation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis.1864 (2): 563-578. DOI: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2017.11.023.
146. Aksoy N, Vural H, Sabuncu T, Aksoy S (2003) Effects of melatonin on oxidative–antioxidative status of tissues in streptozotocin‐induced diabetic rats. Cell Biochem. Funct. 21 (2): 121-125. DOI: 10.1002/cbf.1006.
147. Amin AH, El-Missiry MA, Othman AI (2015) Melatonin ameliorates metabolic risk factors, modulates apoptotic proteins, and protects the rat heart against diabetes-induced apoptosis. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 747: 166-173. DOI: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2014.12.002.
148. Yu L, Gong B, Duan W, Fan C, Zhang J, Li Z, Xue X, Xu Y, Meng D, Li B, Zhang M (2017) Melatonin ameliorates myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury in type 1 diabetic rats by preserving mitochondrial function: role of AMPK-PGC-1α-SIRT3 signaling. Sci. Rep. 7 (1): 1-3. DOI: 10.1038/srep41337.
149. Zhou H, Yue Y, Wang J, Ma Q, Chen Y (2018) Melatonin therapy for diabetic cardiomyopathy: a mechanism involving Syk-mitochondrial complex I-SERCA pathway. Cell Signal. 47: 88-100. DOI: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2018.03.012.
150. Xiong FY, Tang ST, Su H, Tang HQ, Jiang P, Zhou Q, Wang Y, Zhu HQ (2018) Melatonin ameliorates myocardial apoptosis by suppressing endoplasmic reticulum stress in rats with long term diabetic cardiomyopathy. Mol. Med. Rep. 17 (1): 374-381. DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2017.7841.
151. Che H, Wang Y, Li H, Li Y, Sahil A, Lv J, Liu Y, Yang Z, Dong R, Xue H, Wang L (2020) Melatonin alleviates cardiac fibrosis via inhibiting lncRNA MALAT1/miR‐141‐mediated NLRP3 inflammasome and TGF‐β1/Smadssignaling in diabetic cardiomyopathy. The FASEB Journal. 34 (4): 5282-5298. DOI: 10.1096/fj.201902692R.
152. Song YJ, Zhong CB, Wu W (2020) Cardioprotective effects of melatonin: Focusing on its roles against diabetic cardiomyopathy. Biomed. Pharmacother 128: 110260. DOI: 10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110260.
153. Hammes HP, Feng Y, Pfister F, Brownlee M (2011) Diabetic retinopathy: targetingvasoregression. Diabetes 60 (1): 9-16. DOI: 10.1007/s00125-017-4435-8.
154. Mehrzadi S, Motevalian M, Rezaei Kanavi M, Fatemi I, Ghaznavi H, Shahriari M (2018) Protective effect of melatonin in the diabetic rat retina. Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol. 32 (4): 414-421. DOI: 10.1111/fcp.12361.
155. Jiang T, Chang Q, Zhao Z, Yan S, Wang L, Cai J, Xu G (2012) Melatonin-mediated cytoprotection against hyperglycemic injury in Müller cells. PloS One 7 (12): e50661. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0050661.
156. Dehdashtian E, Mehrzadi S, Yousefi B, Hosseinzadeh A, Reiter RJ, Safa M, Ghaznavi H, Naseripour M (2018) Diabetic retinopathy pathogenesis and the ameliorating effects of melatonin; involvement of autophagy, inflammation and oxidative stress. Life Sci. 193: 20-33. DOI: 10.1016/j.lfs.2017.12.001.
157. Jiang T, Chang Q, Cai J, Fan J, Zhang X, Xu G (2016) Protective effects of melatonin on retinal inflammation and oxidative stress in experimental diabetic retinopathy. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2016: 3528274 DOI:10.1155/2016/3528274.
158. Ma Y, Zhao Q, Shao Y, Cao MZ, Zhao M, Wang D (2019) Melatonin inhibits the inflammation and apoptosis in rats with diabetic retinopathy via MAPK pathway. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 23 (3 Suppl): 1-8. DOI: 10.26355/eurrev_202007_22183.
159. Özdemir G, Ergün Y, Bakariş S, Kılınç M, Durdu H, Ganiyusufoğlu E (2014) Melatonin prevents retinal oxidative stress and vascular changes in diabetic rats. Eye 28 (8): 1020-1027. DOI: 10.1038/eye.2014.127.
160. Salido EM, Bordone M, De Laurentiis A, Chianelli M, Keller Sarmiento MI, Dorfman D, Rosenstein RE (2013) Therapeutic efficacy of melatonin in reducing retinal damage in an experimental model of early type 2 diabetes in rats. J. Pineal Res. 54 (2): 179-189. DOI: 10.1111/jpi.12008.
161. Allen DA, Harwood SM, Varagunam M, Raftery MJ, Yaqoob MM (2003) High glucose‐induced oxidative stress causes apoptosis in proximal tubular epithelial cells and is mediated by multiple caspases. FASEB J. 17 (8): 1-21. DOI: 10.1096/fj.02-0130fje.
162. Alqasim AA, Eldin EE, Hammadi SH, Esheba GE (2020) Comparing the renoprotective effects of the antioxidants melatonin, vitamin D and vitamin E in diabetic rats. J. Taibah Univ. Med. Sci. 15 (5): 351-357. DOI: 10.1016/j.jtumed.2020.05.007.
163. Elbe H, Vardi Nİ, Esrefoglu M, Ates B, Yologlu S, Taskapan C (2015) Amelioration of streptozotocin-induced diabetic nephropathy by melatonin, quercetin, and resveratrol in rats. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 34 (1): 100-113. DOI: 10.1177/0960327114531995.
164. Cam M, Yavuz Ö, GuvenA, Ercan F, Bukan N, Üstündag N (2003) Protective effects of chronic melatonin treatment against renal injury in streptozotocin‐induced diabetic rats. J. Pineal Res.35 (3): 212-220. DOI: 10.1034/j.1600-079x.2003.00082.x.
165. Ebaid H, Bashandy SA, Abdel-Mageed AM, Al-Tamimi J, Hassan I, Alhazza IM (2020) Folic acid and melatonin mitigate diabetic nephropathy in rats via inhibition of oxidative stress. Nutr. Metab. 17 (1): 1-4. DOI: 10.1186/s12986-019-0419-7.
166. Onk D, Onk OA, Turkmen K, Erol HS, AyazogluTA, Keles ON, Halici M, Topal E (2016) Melatonin attenuates contrast-induced nephropathy in diabetic rats: the role of interleukin-33 and oxidative stress. Mediators Inflamm. 2016: 9050828. DOI: 10.1155/2016/9050828.
167. Motawi TK, Ahmed SA, Hamed MA, El-Maraghy SA, Aziz WM (2019) Melatonin and/or rowatinex attenuate streptozotocin-induced diabetic renal injury in rats. J. Biomed. Res. 33 (2): 113-121. DOI: 10.7555/JBR.31.20160028.
168. Motawi TK, Ahmed SA, Hamed MA, El-Maraghy SA, Aziz WM (2016) Combination of melatonin and certain drugs for treatment of diabetic nephropathy in streptozotocin-induced diabetes in rats. Diabetol. Int. 7 (4): 413-424. DOI: 10.1007/s13340-016-0268-9.
169. Rashed LA, Elattar S, Eltablawy N, Ashour H, Mahmoud LM, El-Esawy Y (2018) Mesenchymal stem cells pretreated with melatonin ameliorate kidney functions in a rat model of diabetic nephropathy. Biochem. Cell Biol. 96 (5): 564-571. DOI: 10.1139/bcb-2017-0230.
170. Ha H, Yu MR, Kim KH (1999) Melatonin and taurine reduce early glomerulopathy in diabetic rats. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 26 (7-8): 944-950. DOI: 10.1016/s0891-5849(98)00276-7.
171. DeFronzo RA, Goodman AM (1995)Multicenter Metformin Study Group. Efficacy of metformin in patients with non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. N. Engl. J. Med. 333 (9): 541-549. DOI: 10.1056/NEJM199508313330902.
172. de Lima Ávila D, de Araújo GR, Silva M, de Amorim Miranda PH, Diniz MF, Pedrosa ML, Silva ME, de Lima WG, Costa DC (2013) Vildagliptin ameliorates oxidative stress and pancreatic beta cell destruction in type 1 diabetic rats. Arch. Med. Res. 44 (3): 194-202. DOI: 10.1016/j.arcmed.2013.03.004.
173. Marín-Peñalver JJ, Martín-Timón I, Sevillano-Collantes C, del Cañizo-Gómez FJ (2016) Update on the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. World J. Diabetes 7 (17): 354-395. DOI: 10.4239/wjd.v7.i17.354.
174. Wang YW, He SJ, Feng X, Cheng J, Luo YT, Tian L, Huang Q (2017) Metformin: a review of its potential indications. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 11: 2421-2429. DOI: 10.2147/DDDT.S141675.
175. Kadhim HM, Ismail SH, Hussein KI, Bakir IH, Sahib AS, Khalaf BH, Hussain SA (2006) Effects of melatonin and zinc on lipid profile and renal function in type 2 diabetic patients poorly controlled with metformin. J. Pineal Res. 41 (2): 189-193. DOI: 10.1111/j.1600-079X.2006.00353.x.
176. Hussain SA, Khadim HM, Khalaf BH, Ismail SH, Hussein KI, Sahib AS (2006) Effects of melatonin and zinc on glycemic control in type 2 diabetic patients poorly controlled with metformin. Saudi Med. J. 27 (10): 1483-1488. PMID: 17013468.
177. Andrzejewski S, Gravel SP, Pollak M, St-Pierre J (2014) Metformin directly acts on mitochondria to alter cellular bioenergetics. Cancer Metab. 2 (1): 1-4. DOI: 10.1186/2049-3002-2-12.
178. Esteghamati A, Eskandari D, Mirmiranpour H, Noshad S, Mousavizadeh M, Hedayati M, Nakhjavani M (2013) Effects of metformin on markers of oxidative stress and antioxidant reserve in patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes: a randomized clinical trial. Clin. Nutr. 32 (2): 179-185. DOI: 10.1016/j.clnu.2012.08.006.
179. Chakraborty A, Chowdhury S, Bhattacharyya M (2011) Effect of metformin on oxidative stress, nitrosative stress and inflammatory biomarkers in type 2 diabetes patients. Diabetes Res. Clin Pract. 93 (1): 56-62. DOI: 10.1016/j.diabres.2010.11.030. Epub 2010 Dec 13.
180. Diniz Vilela D, Gomes Peixoto L, Teixeira RR, Belele Baptista N, Carvalho Caixeta D, Vieira de Souza A, Machado HL, Pereira MN, Sabino-Silva R, Espindola FS (2016) The role of metformin in controlling oxidative stress in muscle of diabetic rats. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2016: 6978625. DOI:10.1155/2016/6978625.
181. Bonnefont-Rousselot D, Raji B, Walrand S, Gardes-Albert M, Jore D, Legrand A, Peynet J, Vasson MP (2003) An intracellular modulation of free radical production could contribute to the beneficial effects of metformin towards oxidative stress. Metabolism 52 (5): 586-589. DOI: 10.1053/meta.2003.50093.
182. Rösen P, Wiernsperger NF (2006) Metformin delays the manifestation of diabetes and vascular dysfunction in Goto–Kakizaki rats by reduction of mitochondrial oxidative stress. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 22 (4): 323-330. DOI: 10.1002/dmrr.623.
183. Abdulkadir AA, Thanoon IA (2012) Comparative effects of glibenclamide and metformin on C-reactive protein and oxidant/antioxidant status in patients with type II diabetes mellitus. Sultan Qaboos Univ. Med. J. 12 (1): 55-61. DOI: 10.12816/0003088.
184. Han X, Wang B, Sun Y, Huang J, Wang X, Ma W, Zhu Y, Xu R, Jin H, Liu N (2018) Metformin modulates high glucose-incubated human umbilical vein endothelial cells proliferation and apoptosis through AMPK/CREB/BDNF pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 9: 1266. DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2018.01266.
185. Ren H, Shao Y, Wu C, Ma X, Lv C, Wang Q (2020) Metformin alleviates oxidative stress and enhances autophagy in diabetic kidney disease via AMPK/SIRT1-FoxO1 pathway. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 500: 110628. DOI: 10.1016/j.mce.2019.110628.
186. Hardie DG, Hawley SA, Scott JW (2006) AMP‐activated protein kinase–development of the energy sensor concept. J. Physiol. 574 (1): 7-15. DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2006.108944.
187. Leverve XM, Guigas B, Detaille D, Batandier C, Koceir EA, Chauvin C, Fontaine E, Wiernsperger NF (2003) Mitochondrial metabolism and type-2 diabetes: a specific target of metformin. Diabetes Metab.29 (4): 6S88-6S94. DOI: 10.1016/s1262-3636(03)72792-x.
188. Yang M, Darwish T, Larraufie P, Rimmington D, Cimino I, Goldspink DA, Jenkins B, Koulman A, Brighton CA, Ma M, Lam BYH, Coll AP, O'Rahilly S, Reimann F, Gribble FM (Inhibition of mitochondrial function by metformin increases glucose uptake, glycolysis and GDF-15 release from intestinal cells. Sci Rep. 11 (1): 2529. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-81349-7.
189. Docrat TF, Nagiah S, Naicker N, Baijnath S, Singh S, Chuturgoon AA (2020) The protective effect of metformin on mitochondrial dysfunction and endoplasmic reticulum stress in diabetic mice brain. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 875: 173059. DOI: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2020.173059.
190. Batchuluun B, Inoguchi T, Sonoda N, Sasaki S, Inoue T, Fujimura Y, Miura D, Takayanagi R (2014) Metformin and liraglutide ameliorate high glucose-induced oxidative stress via inhibition of PKC-NAD (P) H oxidase pathway in human aortic endothelial cells. Atherosclerosis.232 (1): 156-164. DOI: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2013.10.025.
191. Salman ZK, Refaat R, Selima E, El Sarha A, Ismail MA (2013) The combined effect of metformin and L-cysteine on inflammation, oxidative stress and insulin resistance in streptozotocin-induced type 2 diabetes in rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 714 (1-3): 448-455. DOI: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2013.07.002
192. Cameron AR, Morrison VL, Levin D, Mohan M, Forteath C, Beall C, McNeilly AD, Balfour DJ, Savinko T, Wong AK, Viollet B (2016) Anti-inflammatory effects of metformin irrespective of diabetes status. Circ. Res. 119 (5): 652-665. DOI: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.116.308445.
193. Saisho Y (2015) Metformin and inflammation: its potential beyond glucose-lowering effect. Endocr. Metab. Immune Disord. Drug Targets 15 (3): 196-205. DOI: 10.2174/1871530315666150316124019.
194. Zhou G, Myers R, Li Y, Chen Y, Shen X, Fenyk-Melody J, Wu M, Ventre J, Doebber T, Fujii N, Musi N (2001) Role of AMP-activated protein kinase in mechanism of metformin action. J. Clin. Invest. 108 (8): 1167-1174. DOI: 10.1172/JCI13505.
195. Davis BJ, Xie Z, Viollet B, Zou MH (2006) Activation of the AMP-activated kinase by antidiabetes drug metformin stimulates nitric oxide synthesis in vivo by promoting the association of heat shock protein 90 and endothelial nitric oxide synthase. Diabetes 55 (2): 496-505. DOI: 10.2337/diabetes.55.02.06.db05-1064.
196. Hattori Y, Suzuki K, Hattori S, Kasai K (2006) Metformin inhibits cytokine-induced nuclear factor κB activation via AMP-activated protein kinase activation in vascular endothelial cells. Hypertension 47 (6): 1183-1188. DOI: 10.1161/01.HYP.0000221429.94591.72.
197. Li SN, Wang X, Zeng QT, Feng YB, Cheng X, Mao XB, Wang TH, Deng HP (2009) Metformin inhibits nuclear factor κB activation and decreases serum high-sensitivity C-reactive protein level in experimental atherogenesis of rabbits. Heart vessels 24 (6): 446-453. DOI: 10.1007/s00380-008-1137-7.
198. Chen W, Liu X, Ye S (2016) Effects of metformin on blood and urine pro-inflammatory mediators in patients with type 2 diabetes. J. Inflamm.13 (1): 1-6. DOI: 10.1186/s12950-016-0142-3.
199. Ruggiero-Lopez D, Lecomte M, Moinet G, Patereau G, Lagarde M, Wiernsperger N (1999) Reaction of metformin with dicarbonyl compounds. Possible implication in the inhibition of advanced glycation end product formation. Biochem. Pharmacol. 58 (11): 1765-1773. DOI: 10.1016/s0006-2952(99)00263-4.
200. Beisswenger P, Ruggiero-Lopez D (2003) Metformin inhibition of glycation processes. Diabetes Metab. 29 (4): 6S95-6S103. DOI: 10.1016/s1262-3636(03)72793-1.
201. Ishibashi Y, Matsui T, Takeuchi M, Yamagishi S (2012) Metformin inhibits advanced glycation end products (AGEs)-induced renal tubular cell injury by suppressing reactive oxygen species generation via reducing receptor for AGEs (RAGE) expression. Horm. Metab. Res. 44 (12): 891-895. DOI: 10.1055/s-0032-1321878.
202. Kim SA, Choi HC (2012) Metformin inhibits inflammatory response via AMPK–PTEN pathway in vascular smooth muscle cells. Biochem.Biophys. Res. Commun. 425 (4): 866-872. DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2012.07.165.
203. Hundal RS, Krssak M, Dufour S, Laurent D, Lebon V, Chandramouli V, Inzucchi SE, Schumann WC, Petersen KF, Landau BR, Shulman GI (2000) Mechanism by which metformin reduces glucose production in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 49 (12): 2063-2069. DOI: 10.2337/diabetes.49.12.2063.
204. Takashima M, Ogawa W, Hayashi K, Inoue H, Kinoshita S, Okamoto Y, Sakaue H, Wataoka Y, Emi A, Senga Y, Matsuki Y (2010) Role of KLF15 in regulation of hepatic gluconeogenesis and metformin action. Diabetes 59 (7): 1608-1615. DOI: 10.2337/db09-1679.
205. Cheng JT, Huang CC, Liu IM, Tzeng TF, Chang CJ (2006) Novel mechanism for plasma glucose–lowering action of metformin in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Diabetes 55 (3): 819-825. DOI: 10.2337/diabetes.55.03.06.db05-0934.
206. Heishi M, Hayashi K, Ichihara J, Ishikawa H, Kawamura T, Kanaoka M, Taiji M, Kimura T (2008) Comparison of gene expression changes induced by biguanides in db/db mice liver. J. Toxicol. Sci. 33 (3): 339-347. DOI: 10.2131/jts.33.339.
207. He L, Sabet A, Djedjos S, Miller R, Sun X, Hussain MA, Radovick S, Wondisford FE (2009) Metformin and insulin suppress hepatic gluconeogenesis through phosphorylation of CREB binding protein. Cell 137 (4): 635-646. DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2009.03.016.
208. Madiraju AK, Erion DM, Rahimi Y, Zhang XM, Braddock DT, Albright RA, Prigaro BJ, Wood JL, Bhanot S, MacDonald MJ, Jurczak MJ (2014) Metformin suppresses gluconeogenesis by inhibiting mitochondrial glycerophosphate dehydrogenase. Nature 510 (7506): 542-546. DOI: 10.1038/nature13270.
209. LaMoia TE, Shulman GI (2021) Cellular and molecular mechanisms of metformin action. Endocr. Rev. 42 (1): 77-96. DOI: 10.1210/endrev/bnaa023.
210. Alshawi A, Agius L (2019) Low metformin causes a more oxidized mitochondrial NADH/NAD redox state in hepatocytes and inhibits gluconeogenesis by a redox-independent mechanism. J. Biol. Chem. 294 (8): 2839-2853. DOI:10.1074/jbc.RA118.006670.
211. Li M, Li X, Zhang H, Lu Y (2018) Molecular mechanisms of metformin for diabetes and cancer treatment. Front. Physiol. 9: 1039. DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2018.01039.
212. Batandier C, Guigas B, Detaille D, El-Mir M, Fontaine E, Rigoulet M, Leverve XM (2006) The ROS production induced by a reverse-electron flux at respiratory-chain complex 1 is hampered by metformin. J. Bioenerg. Biomembr. 38 (1): 33-42. DOI: 10.1007/s10863-006-9003-8.
213. Owen MR, Doran E, Halestrap AP (2000) Evidence that metformin exerts its anti-diabetic effects through inhibition of complex 1 of the mitochondrial respiratory chain. Biochem. J. 348 (3): 607-614.PMID: 10839993.
214. Ouyang J, Parakhia RA, Ochs RS (2011) Metformin activates AMP kinase through inhibition of AMP deaminase. J. Biol. Chem. 286 (1): 1-11. DOI:10.1074/jbc.M110.121806.
215. Shaw RJ, Lamia KA, Vasquez D, Koo SH, Bardeesy N, DePinho RA, Montminy M, Cantley LC (2005) The kinase LKB1 mediates glucose homeostasis in liver and therapeutic effects of metformin. Science 310 (5754): 1642-1646. DOI: 10.1126/science.1120781.
216. Kim YD, Park KG, Lee YS, Park YY, Kim DK, Nedumaran B, Jang WG, Cho WJ, Ha J, Lee IK, Lee CH (2008) Metformin inhibits hepatic gluconeogenesis through AMP-activated protein kinase–dependent regulation of the orphan nuclear receptor SHP. Diabetes 57 (2): 306-314. DOI: 10.2337/db07-0381.
217. Rines AK, Sharabi K, Tavares CD, Puigserver P (2016) Targeting hepatic glucose metabolism in the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 15 (11): 786-804. DOI: 10.1038/nrd.2016.151.
218. An H, He L (2016) Current understanding of metformin effect on the control of hyperglycemia in diabetes. J. Endocrinol. 228 (3): R97-106. DOI:10.1530/JOE-15-0447.
219. Polianskyte-Prause Z, Tolvanen TA, Lindfors S, Dumont V, Van M, Wang H, Dash SN, Berg M, Naams JB, Hautala LC,Nisen H (2019) Metformin increases glucose uptake and acts renoprotectively by reducing SHIP2 activity. FASEB J. 33 (2): 2858-2869. DOI: 10.1096/fj.201800529RR.
220. Wiernsperger NF, Bailey CJ (1999) The antihyperglycaemic effect of metformin. Drugs 58 (1): 31-39. DOI: 10.2165/00003495-199958001-00009.
221. Diaz-Morales N, Rovira-Llopis S, Bañuls C, Lopez-Domenech S, Escribano-Lopez I, Veses S, Jover A, Rocha M, Hernandez-Mijares A, Victor VM (2017) Does metformin protect diabetic patients from oxidative stress and leukocyte-endothelium interactions?. Antioxid. Redox. Signal 27 (17): 1439-1445. DOI: 10.1089/ars.2017.7122.
222. Diaz-Morales N, Iannantuoni F, Escribano-Lopez I, Banuls C, Rovira-Llopis S, Sola E, Rocha M, Hernandez-Mijares A, Victor VM (2018) Does metformin modulate endoplasmic reticulum stress and autophagy in type 2 diabetic peripheral blood mononuclear cells?. Antioxid. Redox. Signal 28 (17): 1562-1569.DOI: 10.1089/ars.2017.7409.
223. Simon-Szabó L, Kokas M, Mandl J, Kéri G, Csala M (2014) Metformin attenuates palmitate-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress, serine phosphorylation of IRS-1 and apoptosis in rat insulinoma cells. PLoS One 9 (6): e97868. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0097868.
224. Moon JS, Karunakaran U, Elumalai S, Lee IK, Lee HW, Kim YW, Won KC (2017) Metformin prevents glucotoxicity by alleviating oxidative and ER stress–induced CD36 expression in pancreatic beta cells. J. Diab. Complicat. 31 (1): 21-30. DOI: 10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2016.09.001.
225. Quentin T, Steinmetz M, Poppe A, Thoms S (2012) Metformin differentially activates ER stress signaling pathways without inducing apoptosis. Dis. Model Mech. 5 (2): 259-269. DOI: 10.1242/dmm.008110.
226. Jung TW, Lee MW, Lee YJ, Kim SM (2012) Metformin prevents endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis through AMPK-PI3K-c-Jun NH2 pathway. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 417 (1): 147-152. DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2011.11.073.
227. Li A, Zhang S, Li J, Liu K, Huang F, Liu B (2016) Metformin and resveratrol inhibit Drp1-mediated mitochondrial fission and prevent ER stress-associated NLRP3 inflammasome activation in the adipose tissue of diabetic mice. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 434: 36-47. DOI: 10.1016/j.mce.2016.06.008.
228. Kitabchi AE, Temprosa M, Knowler WC, Kahn SE, Fowler SE, Haffner SM, Andres R, Saudek C, Edelstein SL, Arakaki R, Murphy MB, Shamoon H (2005) Diabetes Prevention Program Research Group Role of insulin secretion and sensitivity in the evolution of type 2 diabetes in the diabetes prevention program: effects of lifestyle intervention and metformin. Diabetes 54 (8): 2404-2414. DOI: 10.2337/diabetes.54.8.2404.
229. Yang X, Xu Z, Zhang C, Cai Z, Zhang J (2017) Metformin, beyond an insulin sensitizer, targeting heart and pancreatic β cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis.1863 (8): 1984-1990. DOI: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2016.09.019. Epub 2016 Oct 1.
230. Hashemitabar M, Bahramzadeh S, Saremy S, Nejaddehbashi F (2015) Glucose plus metformin compared with glucose alone on β cell function in mouse pancreatic islets. Biomed. Rep. 3 (5): 721-725. DOI: 10.3892/br.2015.476.
231. Patanè G, Piro S, Rabuazzo AM, Anello M, Vigneri R, Purrello F (2000) Metformin restores insulin secretion altered by chronic exposure to free fatty acids or high glucose: a direct metformin effect on pancreatic beta-cells. Diabetes 49 (5): 735-740. DOI: 10.2337/diabetes.49.5.735.
232. Marchetti P, Del Guerra S, Marselli L, Lupi R, Masini M, Pollera M, Bugliani M, Boggi U, Vistoli F, Mosca F, Del Prato S (2004) Pancreatic islets from type 2 diabetic patients have functional defects and increased apoptosis that are ameliorated by metformin. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 89 (11): 5535-5541. DOI: 10.1210/jc.2004-0150.
233. Lupi R, Del Guerra S, Tellini C, Giannarelli R, Coppelli A, Lorenzetti M, Carmellini M, Mosca F, Navalesi R, Marchetti P (1999) The biguanide compound metformin prevents desensitization of human pancreatic islets induced by high glucose. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 364 (2-3): 205-209. DOI: 10.1016/s0014-2999(98)00807-3.
234. Lablanche S, Cottet-Rousselle C, Lamarche F, Benhamou PY, Halimi S, Leverve X, Fontaine E (2011) Protection of pancreatic INS-1 β-cells from glucose-and fructose-induced cell death by inhibiting mitochondrial permeability transition with cyclosporin A or metformin. Cell Death Dis.2 (3): e134. DOI: 10.1038/cddis.2011.15.
235. Sanchez-Rangel E, Inzucchi SE (2017) Metformin: clinical use in type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia 60 (9): 1586-1593. DOI: 10.1007/s00125-017-4336-x.
236. McCreight LJ, Bailey CJ, Pearson ER (2016) Metformin and the gastrointestinal tract. Diabetologia 59 (3): 426-435. DOI: 10.1007/s00125-015-3844-9.
237. Shurrab NT, Arafa ES (2020) Metformin: A review of its therapeutic efficacy and adverse effects. Ob. Med.17: 100186. DOI: 10.1016/j.obmed.2020.100186.
238. DeFronzo R, Fleming GA, Chen K, Bicsak TA (2016) Metformin-associated lactic acidosis: Current perspectives on causes and risk. Metabolism 65 (2): 20-29. DOI: 10.1016/j.metabol.2015.10.014.
239. De Jager J, Kooy A, Lehert P, Wulffelé MG, Van der Kolk J, Bets D, Verburg J, Donker AJ, Stehouwer CD (2010) Long term treatment with metformin in patients with type 2 diabetes and risk of vitamin B-12 deficiency: randomised placebo controlled trial. BMJ 340: c2181. DOI: 10.1136/bmj.c2181.
240. Hsu WH, Hsiao PJ, Lin PC, Chen SC, Lee MY, Shin SJ (2018) Effect of metformin on kidney function in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and moderate chronic kidney disease. Oncotarget 9 (4): 5416-5423. DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.23387.
241. Bubenik GA (2001) Localization, physiological significance and possible clinical implication of gastrointestinal melatonin. Neurosignals 10 (6): 350-366. DOI: 10.1159/000046903
242. Rahman A, Hasan AU, Kobori H (2019) Melatonin in chronic kidney disease: A promising chronotherapy targeting the intrarenal renin–angiotensin system. Hypertens. Res. 42 (6): 920-923. DOI: 10.1038/s41440-019-0223-9.
243. Raza Z, Naureen Z (2020) Melatonin ameliorates the drug induced nephrotoxicity: Molecular insights. Nefrología 40 (1): 12-25. DOI: 10.1016/j.nefro.2019.06.009.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
For all articles published in Melatonin Res., copyright is retained by the authors. Articles are licensed under an open access Creative Commons CC BY 4.0 license, meaning that anyone may download and read the paper for free. In addition, the article may be reused and quoted provided that the original published version is cited. These conditions allow for maximum use and exposure of the work, while ensuring that the authors receive proper credit.
In exceptional circumstances articles may be licensed differently. If you have specific condition (such as one linked to funding) that does not allow this license, please mention this to the editorial office of the journal at submission. Exceptions will be granted at the discretion of the publisher.


