Retinoic Acid-Related Orphan Receptor alpha 1 (RORα1) Induction of AKR1C3 Promotes MCF-7 Breast Cancer Cell Proliferation and Tamoxifen-Resistance which is Suppressed by Melatonin
Melatonin inhibits RORα1 and AKR1C3 expression
Abstract
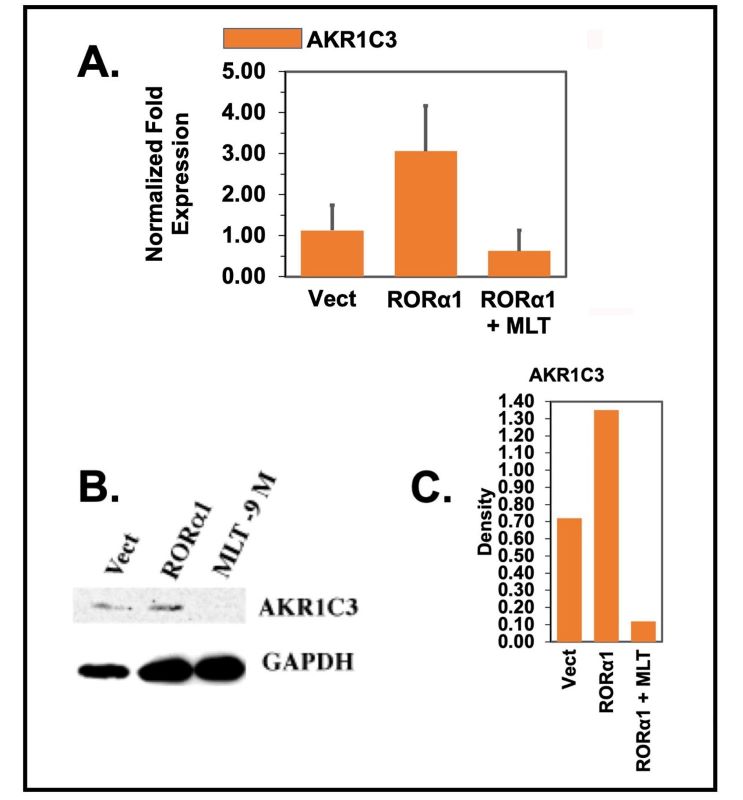
The retinoic acid-related orphan receptors alpha (RORa) are members of the steroid/thyroid nuclear receptor super-family and core components of the circadian timing system. In the present study, we continue to investigate the role of RORas in human breast cancer. Assays using the RORa response element (RORE)-tk-luciferase reporter demonstrate the functionality of the RORa1 in MCF-7 breast cancer cells and that over-expression of RORa1 stimulates MCF-7 human breast cancer cell proliferation. Genomic analysis revealed that RORα1 over-expression regulated the transcription of numerous genes in MCF-7 breast cancer cells including increasing the expression of connexin 43 (CX43), aldo-keto reductases 1C1 (AKR1C1), and AKR1C3. Furthermore, administration of the pineal hormone melatonin represses RORa1 induction of CX43, AKR1C1, and AKR1C3 in MCF-7 cells. AKR1C3 has been reported to impact in intra-tumoral production of androgens and estrogens and thus, might promote Tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer. Over-expression of RORa1 and subsequently AKR1C3 does promote Tamoxifen resistance, which can be inhibited by melatonin administration.
References
2. Osborne CK, Hobbs K, and Clark GM (1985) Effect of estrogens and antiestrogens on growth of human breast cancer cells in athymic nude mice. Cancer Res. 45: 584-590.
3. Dickson RB, Lippman ME (1995) Growth factors in breast cancer. Endocrine Rev. 16: 559-589.
4. Dai J, Ram PT, Yuan L, Spriggs LL, Hill SM (2001) Transcriptional repression of ROR activity in human breast cancer cells by melatonin. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 176: 111-120.
5. Giguere V, Tini M, Flock G, Ong ES, Evans RM, Otulakowski G (1994) Isoform-specific amino-terminal domains dictate DNA-binding properties of ROR, a novel family of orphan nuclear receptors. Genes Dev. 8: 538-553.
6. Hamilton BA, Frankel WN, Kerrebrock AW, Hawkins TL, FitzHugh W, Kusumi K, Russell LB, Mueller KL, van Berkel V, Birren BW, Kruglyak L, Lander ES (1996) Disruption of the nuclear hormone receptor ROR alpha in staggerer mice. Nature 379: 736-739.
7. Giguere V, Beatty B, Squire J, Copeland NG, Jenkins NA (1995) The orphan nuclear receptor ROR alpha (ROR) maps to a conserved region of homology on human chromosome 15q21-q22 and mouse chromosome 9. Genomics 28: 596-598.
8. Raspe E, Mautino G, Duval C, Fontaine C, Duez H, Barbier O, Monte D, Fruchart J, Fruchat JC, Staels B (2002) Transcriptional regulation of human Rev-erb gene expression by the orphan nuclear receptor ROR. J. Biol. Chem. 277: 49275-49281.
9. Becker-Andre M, Andre E, DeLamarter JF (1993) Identification of nuclear receptor mRNAs by RT-PCR amplification of conserved zinc-finger motif sequences. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 194: 1371-1379.
10. Knower KC, Chand AL, Eriksson N, Takagi K, Miki Y, Sasano H, Visvader JE, Lindeman GJ, Funder JW, Fuller PJ, Simpson ER, Tilley WD, Leedman PJ, Graham J, Muscat GE, Clarke CL, Clyne CD (2013) Distinct nuclear receptor expression in stroma adjacent to breast tumors. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 142: 211-23.
11. Jetten AM (2009) Retinoid-related orphan receptors (RORs): critical roles in development, immunity, circadian rhythm, and cellular metabolism. Nucl. Recept. Signal 7: e003.
12. Schrader M, Danielsson C, Wiesenberg I, Carlberg C (1996) Identification of natural monomeric response elements of the nuclear receptor RZR/ROR they also bind COUP-TF homodimers. J. Biol. Chem. 271: 19732-19736.
13. Kleinman HK, Weeks BS, Schnaper HW, Kibbey MC, Yamamura K, Grant DS (1993) The laminins: a family of basement membrane glycoproteins important in cell differentiation and tumor metastases. Vitam. Horm. 47: 161-186.
14. Paravicini G, Steimayr M, Andre E, Becker-Andre M (1996) The metastasis suppressor candidate nucleotide diphosphate kinase NM23 specifically interacts with members of the ROR/RZR nuclear orphan receptor subfamily. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 227: 82-87.
15. Steeg PS, Zhou Q (1999) Cyclins and breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 52: 17-28.
16. Odawara H, Iwasaki T, Horiguchi J, Rokutanda N, Hirooka K, Miyazaki W, Koibuchi Y, Shimokawa N, Iino Y, Takeyoshi I, Koibuchi N (2009) Activation of aromatase expression by retinoic acid receptor-related orphan receptor (ROR) alpha in breast cancer cells: identification of a novel ROR response element. J. Biol. Chem. 284: 17711-17719.
17. Koibuchi N, Liu Y, Fukuda H, Takeshita A, Yen PM, Chin WW (1999) ROR augments thyroid hormone receptor-mediated transcriptional activation. Endocrinology 140: 1356-1364.
18. Tini M, Fraser RA, Giguere V (1995) Functional interactions between retinoic acid receptor-related orphan receptor (ROR) and the retinoic acid receptors in the regulation of the F-crystalin promoter. J. Biol. Chem. 270: 20156-20161.
19. Cadenas C1, van de Sandt L, Edlund K, Lohr M, Hellwig B, Marchan R, Schmidt M, Rahnenführer J, Oster H, Hengstler JG (2014) Loss of circadian clock gene expression is associated with tumor progression in breast cancer. Cell Cycle 13: 3282-3291.
20. Xiang S, Mao L, Duplessis T, Yuan L, Dauchy R, Dauchy E, Blask DE, Frasch T, Hill SM (2012) Oscillation of clock and clock controlled genes induced by serum shock in human breast epithelial and breast cancer cells: regulation by melatonin. Breast Cancer (Auckl) 6: 137-150.
21. Kallen JA, Schlaeppi JM, Bitsch F, Geisse S, Geiser M, Delhon I, Fournier B (2002) X-ray structure of the hRORalpha LBD at 1.63A: structural and functional data that cholesterol or a cholesterol derivative is the natural ligand of RORalpha. Structure 10: 1697-1707.
22. Kane CD, Means AR (2000) Activation of orphan receptor-mediated transcription by Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein. EMBO J. 19: 691-701.
23. Becker-Andre M, Wiesenberg I, Schaeren-Wiemers N, Andre E, Missbach M, Saurat JH, Carlberg C (1994) Pineal gland hormone melatonin binds and activates an orphan nuclear receptor superfamily. J. Biol. Chem. 269: 28531-28534.
24. Hill SM, Blask DE (1988) Effects of the pineal hormone on the proliferation and morphological characteristics of human breast cancer cells (MCF-7) in culture. Cancer Res. 48: 6121–6126.
25. Becker-Andre M, Wiesenberg I, Schaeren-Wiemers N, Andre E, Missbach M, Saurat JH, Carlberg C (1997) Errattum, Pineal gland hormone melatonin binds and activates an orphan nuclear receptor superfamily. J. Biol. Chem. 272: 16707.
26. Hill SM, Belancio VP, Dauchy RT, Xiang S, Brimer S, Mao L, Hauch A, Lundberg PW, Summers W, Yuan L, Frasch T, Blask DE (2015) Melatonin: an inhibitor of breast cancer. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 22: 183-204.
27. Hill SM, Blask DE, Xiang S, Yuan L, Mao L, Dauchy RT, Dauchy EM, Frasch T, Duplesis T (2011) Melatonin and associated signaling pathways that control normal breast epithelium and breast cancer. J. Mammary Gland Biol. Neoplasia 16: 235-245.
28. Dong C, Yuan L, Dai J, Lai L, Mao L, Xiang S, Rowan B, Hill SM (2012) Melatonin inhibits mitogenic cross-talk between retinoic acid-related orphan receptor alpha (RORalpha) and ERalpha in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells. Steroids 75: 944-951.
29. Rižner TL, Penning TM (2014) Role of aldo-keto reductase family 1 (AKR1) enzymes in human steroid metabolism. Steroids 79: 49-63.
30. Teleki I, Szasz AM, Maros ME, Gyorffy B, Kulka J, Meggyeshazi N, Kiszner G, Balla P, Samu A, Krenacs T (2014) Correlations of differentially expressed gap junction connexins Cx26, Cx30, Cx32, Cx43 and Cx46 with breast cancer progression and prognosis. PLoS One 10: e112541.
31. Fu Y, Shao ZM, He QZ, Jiang BQ, Wu Y, Zhuang ZG (2015) Hsa-miR-206 represses the proliferation and invasion of breast cancer cells by targeting Cx43. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci 19: 2091-2104.
32. Stoletov K, Strnadel J, Zardouzian E, Momiyama M, Park FD, Kelber JA, Pizzo DP, Hoffman R, VandenBerg SR, Klemke RL (2013) Role of connexins in metastatic breast cancer and melanoma brain colonization. J. Cell Sci. 126: 904-913.
33. Gold DA, Baek SH, Schork NJ, Rose DW, Larsen DD, Sachs BD, Rosenfeld MG, Hamilton BA (2003) RORalpha coordinates reciprocal signaling in cerebellar development through sonic hedgehog and calcium-dependent pathways. Neuron 40: 1119-1131.
34. Pon CK, Firth SM, Baxter RC (2015) Involvement of insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 in peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma-mediated inhibition of breast cancer cell growth. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 399: 354-361.
35. Vivacqua A, Lappano R, De Marco P, Sisci D, Aquila S, De Amicis F, Fuqua SA, Andò S, Maggiolini M (2009) G protein-coupled receptor 30 expression is up-regulated by EGF and TGF alpha in estrogen receptor alpha-positive cancer cells. Mol. Endocrinol. 23: 1815-1826.
36. Dunn LK, Mohammad KS, Fournier PG, McKenna CR, Davis HW, Niewolna M, Peng XH, Chirgwin JM, Guise TA (2009) Hypoxia and TGF-beta drive breast cancer bone metastases through parallel signaling pathways in tumor cells and the bone microenvironment. PLoS One 4: e6896.
37. Buijs JT, Henriquez NV, van Overveld PG, van der Horst G, Que I, Schwaninger R, Rentsch C, Ten Dijke P, Cleton-Jansen AM, Driouch K, Lidereau R, Bachelier R, Vukicevic S, Clézardin P, Papapoulos SE, Cecchini MG, Löwik CW, van der Pluijm G (2007) Bone morphogenetic protein 7 in the development and treatment of bone metastases from breast cancer. Cancer Res. 67: 8742-8751.
38. Zarzynska JM (2014) Two faces of TGF-beta1 in breast cancer. Mediators Inflamm. 2014: 141747.
39. Cerliani JP, Guillardoy T, Giulianelli S, Vaque JP, Gutkind JS, Vanzulli SI, Martins R, Zeitlin E, Lamb CA, Lanari C (2011) Interaction between FGFR-2, STAT5, and progesterone receptors in breast cancer. Cancer Res. 71: 3720-3731.
40. Tannheimer SL, Rehemtulla A, Ethier SP (2000) Characterization of fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 overexpression in the human breast cancer cell line SUM-52PE. Breast Cancer Res. 2: 311-320.
41. Momeny M, Saunus JM, Marturana F, McCart Reed AE, Black D, Sala G, Iacobelli S, Holland JD, Yu D, Da Silva L, Simpson PT, Khanna KK, Chenevix-Trench G, Lakhani SR (2015) Heregulin-HER3-HER2 signaling promotes matrix metalloproteinase-dependent blood-brain-barrier transendothelial migration of human breast cancer cell lines. Oncotarget 6: 3932-3946.
42. Pathak P, Li T, Chiang JY (2013) Retinoic acid-related orphan receptor α regulates diurnal rhythm and fasting induction of sterol 12α-hydroxylase in bile acid synthesis. J. Biol. Chem. 288: 37154-37165.
43. Wada T, Kang HS, Angers M, Gong H, Bhatia S, Khadem S, Ren S, Ellis E, Strom SC, Jetten AM, Xie W (2008) Identification of oxysterol 7alpha-hydroxylase (Cyp7b1) as a novel retinoid-related orphan receptor alpha (RORalpha) (NR1F1) target gene and a functional cross-talk between RORalpha and liver X receptor (NR1H3). Mol. Pharmacol. 73: 891-899.
44. Moy I, Lin Z, Rademaker AW, Reierstad S, Khan SA, Bulun SE (2013) Expression of estrogen-related gene markers in breast cancer tissue predicts aromatase inhibitor responsiveness. PLoS One 8: e77543.
45. Raspe E, Duez H, Gervois P, Fievet C, Fruchart J-C, Besnard S, Mariani J, Tedgui A, Staels B (2001) Transcriptional regulation of apolipoprotein C-III gene expression by the orphan nuclear receptor RORalpha. J. Biol. Chem. 276: 2865-2871.
46. Need EF, Selth LA, Harris TJ, Birrell SN, Tilley WD, Buchanan G (2012) Research resource: interplay between the genomic and transcriptional networks of androgen receptor and estrogen receptor α in luminal breast cancer cells. Mol. Endocrinol. 26: 1941-1952.
47. Wiesenberg I, Missbach M, Kahlen JP, Schräder M, Carlberg C (1995) Transcriptional activation of the nuclear receptor RZR alpha by the pineal gland hormone melatonin and identification of CGP 52608 as a synthetic ligand. Nucleic Acids Res. 23: 327-333.
48. Wang S, Yang Q, Fung KM, Lin HK (2008) AKR1C2 and AKR1C3 mediated prostaglandin D2 metabolism augments the PI3K/Akt proliferative signaling pathway in human prostate cancer cells. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 289: 60-66.
49. Vergote IB, Laekeman GM, Keersmaekers GH, Uyttenbroeck FL, Vanderheyden JS, Albertyn GP, Haensch CF, De Roy GJ, Herman AG (1985) Prostaglandin F2 alpha in benign and malignant breast tumours. Br. J. Cancer 51: 827-836.
50. Coquenlorge S, Van Landeghem L, Jaulin J, Cenac N, Vergnolle N, Duchalais E, Neunlist M, Rolli-Derkinderen M (2016) The arachidonic acid metabolite 11β-Prostaglandin F2α controls intestinal epithelial healing: deficiency in patients with Crohn's disease. Sci. Rep. 6: 25203.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
For all articles published in Melatonin Res., copyright is retained by the authors. Articles are licensed under an open access Creative Commons CC BY 4.0 license, meaning that anyone may download and read the paper for free. In addition, the article may be reused and quoted provided that the original published version is cited. These conditions allow for maximum use and exposure of the work, while ensuring that the authors receive proper credit.
In exceptional circumstances articles may be licensed differently. If you have specific condition (such as one linked to funding) that does not allow this license, please mention this to the editorial office of the journal at submission. Exceptions will be granted at the discretion of the publisher.


